You will rubber sheet a newly imported set of street features to match an existing feature class of street features.
Arcgis rubber sheet features.
In the modify features pane transform includes linear and natural neighbor interpolation methods for rubber sheeting features.
Two rubbersheeting options are supported.
Natural neighbor and linear.
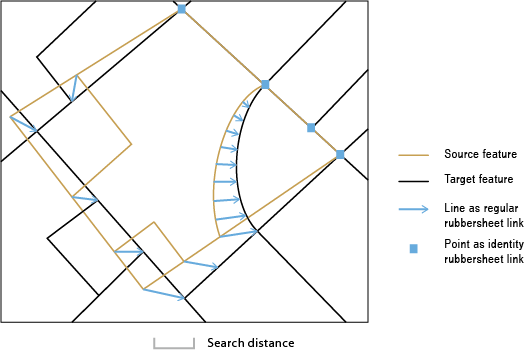
Rubbersheeting makes spatial adjustments to align the input feature locations with more accurate target feature locations based on the specified rubbersheet links.
In some cases you may not want some features to move at all as they may already be aligned.
The input link features represent the regular links.
Identity links can be used to help hold features in certain locations.
Rubbersheeting makes spatial adjustments to align the input feature locations with more accurate target feature locations based on the specified rubbersheet links.
Setting up the data and rubbersheeting options prerequisite.
This exercise will show you how to rubber sheet data by using displacement links multiple displacement links and identity links.
Two point displacement links define the origin and target location of the features you are transforming.
The closer features are to displacement links the farther they will move.
The input link features represent the regular links.
Additionally a rubbersheet can be confined to a polygonal area.
You can transform features that are visible and editable by selecting them or transform all features on specified layers.